- Docs>
- Kakao Login>
- JavaScript
menu
Getting started
Kakao Developers
Login
- Concepts
- Utilize
- Prerequisites
- REST API
- JavaScript
- Before you begin
- Login
- Set token
- Logout
- Unlink
- Retrieve user information
- Shipping address
- Store user information
- Request additional consent
- Retrieve consent details
- Revoke consent
- Get consent to desired service terms
- Retrieve consent details for service terms
- Revoke consent for service terms
- Advanced: Manual signup
- Android
- iOS
- Flutter
- Webhook
- Design Guide
- FAQ
- Error code
Communication
Advertisement
- Concepts
- Ad creation: Ad account
- Ad creation: Campaign
- Ad creation: Ad group
- Targeting for ad group
- Custom audience targeting for ad group
- Ad creation: Creative common
- Ad creation: Display creative
- Ad creation: Message creative
- Ad creation: Personalized message creative
- Bizboard landing settings
- Report
- Message management
- Personalized message management
- Message ad management
- Message ad operation
- Ad View management
- Business Form linkage management
- Pixel & SDK linkage management
- Audience management
- Engagement targeting management
- Customer file management
- Friend group management
- Ad account management
- Reference
- Type information
- Error code
Kakao Login


JavaScript SDK
This document describes how to integrate Kakao Login APIs into your service with Kakao SDK for JavaScript ("JavaScript SDK").
You can test the features described in this document in [Tools] > [JS SDK demo] menu.
For a Kakao Login button, you can download the resources provided by Kakao or customize buttons according to your service user interface by referring to the Design Guide.
Before you begin
Understand login flow
To integrate Kakao Login into your web page with the JavaScript SDK, you need to fully understand how Kakao Login works by referring to REST API > Before you begin.
On mobile devices where Kakao Talk is installed, users can use the Kakao Simple Login function. Here is the flow of Kakao Simple Login.
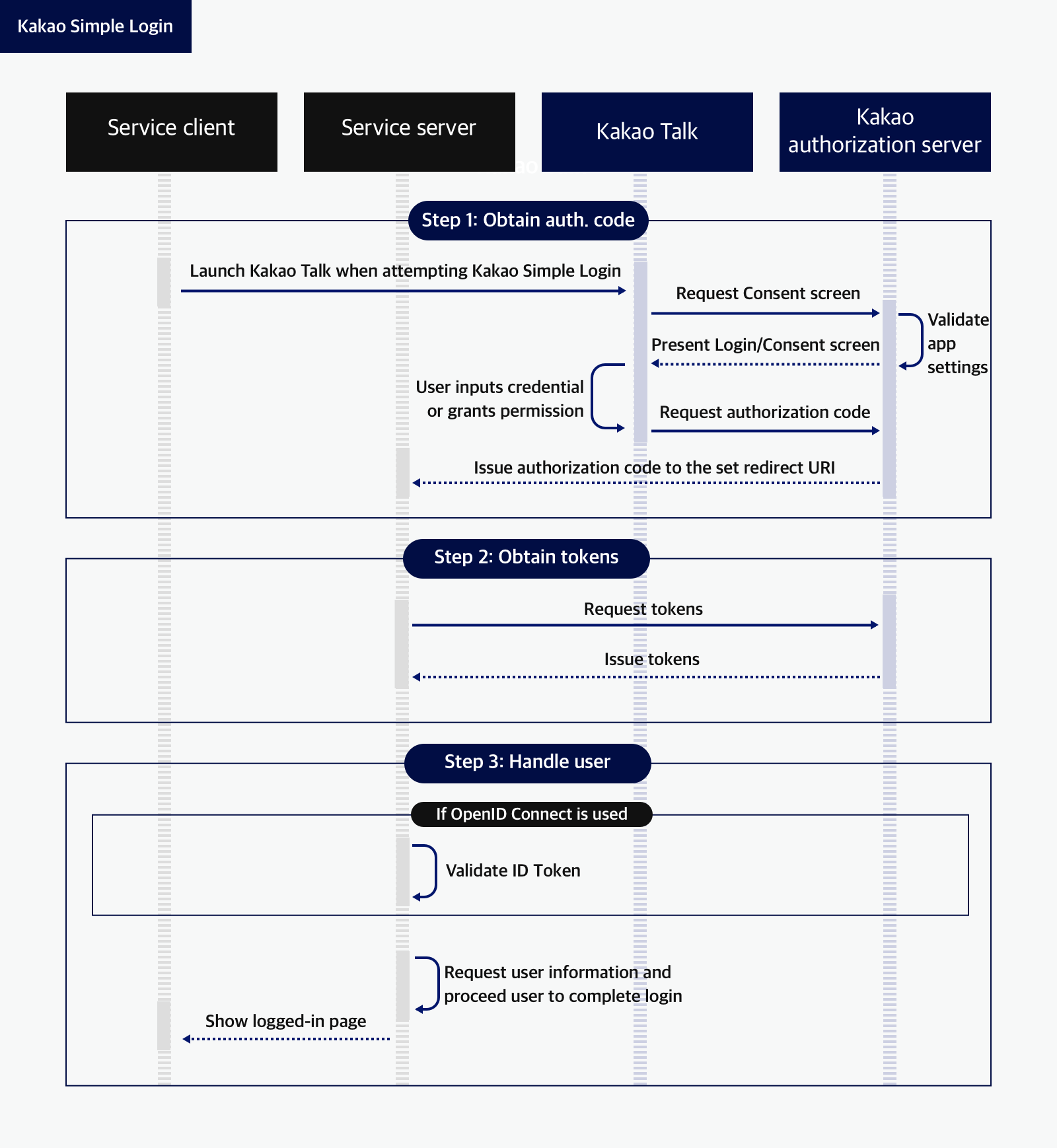
1. Obtain an authorization code
If a user attempts Kakao Simple Login, Kakao.Auth.authorize() is invoked. Then, Kakao Talk is launched and the login page is prompted to the user.
Once the user approves permissions by clicking [Accept and Continue], the Kakao authorization server validates the user’s credentials and issues an authorization code to the specified redirect URI.
If Kakao Talk is not installed on a user's device, the Kakao Login page where the user can log in with a Kakao ID and password is open.
2. Obtain tokens
Implement a process the Get token by using a REST API.
When you request to exchange the authorization code for tokens, the Kakao authorization server validates the request and issues an access token and a refresh token.
3. Handle users to complete login
When an access token is issued, you can call the Retrieving user information API by passing the issued access token. With the user data returned to this API, you can check if the user is registered in your service.
For a new user, register the user in your service's user database as a new member. For a registered user, you can create a login session for the user in your service and show a login page. To see how to handle users depending on the registration status, refer to Link.
The Kakao Login API functions to authenticate users on the Kakao platform and links their accounts with your app so that they can use your service. However, those who do not have Kakao Accounts need to create a new account in your service. In this case, you need to implement the process of creating a new account and updating the user information in your own service.
Login
Basic information
| Reference | App setting |
|---|---|
Kakao.Auth.authorize()Kakao.Auth.setAccessToken() |
Install Initialize |
| Permission | Prerequisite | Kakao Login | User consent |
|---|---|---|---|
| - | JavaScript key Activate Kakao Login Set Redirect URI Manage consent items Advanced: Activate OpenID Connect(Optional) Set Simple Signup(for Kakao Sync) |
Required | Required: Required consent item |
Simple Login
Authenticate a user through Kakao Talk without inputting the Kakao Account information and get an authorization code.
Request
For the Simple Login function, call the Kakao.Auth.authorize() function. If Kakao.Auth.authorize() is invoked, Kakao Talk is launched and the Consent screen is presented.
Response
If a user consents to the provision of their personal information and the use of your service, the Kakao authorization server issues the authorization code to the Redirect URI of the service server with the HTTP response status code 302.
Sample
Kakao.Auth.authorize({
redirectUri: '${REDIRECT_URI}',
});
Get token
Gets tokens with the obtained authorization code. After Simple Login, request the GET token API with the obtained authorization code to complete the login.
When you call 'Kakao.Auth.authorize' through JavaScript SDK, you must use your JavaScript key used to initialize the SDK. However, when you request the Get token API, use your REST API key.
Set token
Assigns the access token to SDK. To to call the Kakao APIs, you need to assign your access token to SDK.
Request
Call the Kakao.Auth.setAccessToken() function with the access token passed in the login response.
Sample
Kakao.Auth.setAccessToken('${ACCESS_TOKEN}');
Additional Feature
Additional features for Simple Login are below.
Request additional consent
You can request consent to access permission or specific personal information if the user has not agreed when the user logged in with Kakao. Call the authorize() function with the scopes you want to request consent through the scope parameter.
Kakao.Auth.authorize({
redirectUri: '${REDIRECT_URI}',
scope: 'account_email,gender',
});
Auto-login from Kakao Talk
To request Auto-login from Kakao Talk, call the authorize() function and set prompt parameter to none.
Kakao.Auth.authorize({
redirectUri: '${REDIRECT_URI}',
prompt: 'none',
});
If the user is not registered to the app, the following error response will be passed to the redirect_uri. In this case, the user should sign in to the service manually.
HTTP/1.1 302 Found
Content-Length: 0
Location: ${REDIRECT_URI}?error=consent_required&error_description=user%20consent%20required.
Get consent to desired service terms
This API is only allowed for the service that adopted Kakao Sync.
This API enables you to request consent to specific service terms that a user has not consented to, regardless of whether the user has already signed up. Pass serviceTerms as a parameter to the authorize() function. Make sure to include all tags of the service terms needed to get consent in a single String format by separating respective tags by comma(,).
Kakao.Auth.authorize({
redirectUri: '${REDIRECT_URI}',
serviceTerms: 'tag1,tag2',
});
Reauthentication login
To reauthenticate the user, set prompt to login. The user will log in again with Kakao Account even though already logged in.
Kakao.Auth.authorize({
redirectUri: '${REDIRECT_URI}',
prompt: 'login',
});
Provide login hint
To fill in the ID automatically, use the loginHint parameter. The value of the loginHint parameter will be entered in the Kakao Account login page.
Kakao.Auth.authorize({
redirectUri: '${REDIRECT_URI}',
loginHint: '${HINT}'
});
Using login hint with auto-login
The loginHint and prompt parameters can be used together.
Kakao.Auth.authorize({
redirectUri: '${REDIRECT_URI}',
prompt: 'none',
loginHint: '${HINT}',
});
Kakao Account easy login
To request Kakao Account easy login, set the prompt parameter to select_account.
Kakao.Auth.authorize({
redirectUri: '${REDIRECT_URI}',
prompt: 'select_account',
});
Logout
Basic information
| Reference | App setting |
|---|---|
logout() |
Install Initialize |
| Permission | Prerequisite | Kakao Login | User consent |
|---|---|---|---|
| - | JavaScript key Activate Kakao Login |
Required | - |
Logs out the user by revoking the tokens stored in the JavaScript SDK. After logout, you cannot call Kakao APIs with the user's information.
Kakao.Auth.logout() makes the tokens expire, not make a user log out from your service or Kakao Account. Therefore, you need to implement the logout process internally in your service.
Request
Call the Kakao.Auth.logout() function.
Response
Kakao.Auth.logout() returns Promise. If the promise is fulfilled, the tokens issued during the login process expire, and the user is logged out. After the user is logged out, you cannot call the Kakao APIs using the access token.
Sample
Kakao.Auth.logout()
.then(function(response) {
console.log(Kakao.Auth.getAccessToken()); // null
})
.catch(function(error) {
console.log('Not logged in.');
});
Unlink
Basic information
| Reference | App setting |
|---|---|
Kakao.API.request() |
Install Initialize |
| Permission | Prerequisite | Kakao Login | User consent |
|---|---|---|---|
| - | JavaScript key Activate Kakao Login |
Required | - |
Withdraws the user's consent and revokes the issued access and refresh tokens. For more details, see Unlink.
Request
To unlink a user's Kakao Account from your app, call the Kakao.API.request() function. The available parameters are below.
Parameter
| Name | Type | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|---|
| url | String |
Fixed to /v1/user/unlink. |
O |
Response
Kakao.API.request() returns Promise. If the promise is fulfilled, the user's service user ID is returned.
Sample
Kakao.API.request({
url: '/v1/user/unlink',
})
.then(function(response) {
console.log(response);
})
.catch(function(error) {
console.log(error);
});
Retrieve user information
Basic information
| Reference | App setting |
|---|---|
Kakao.API.request() |
Install Initialize |
| Permission | Prerequisite | Kakao Login | User consent |
|---|---|---|---|
| - | JavaScript key Activate Kakao Login Manage consent items |
Required | Required: All consent items to request user information |
Retrieves Kakao Account information of a user who is logged into Kakao.
Request
To retrieve the Kakao Account information of a logged-in user, call the kakao.API.request() function. The available parameters are below.
Parameter
| Name | Type | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|---|
| url | String |
Fixed to /v2/user/me. |
O |
| data | Object |
Object that contains the parameter to be passed when requesting the API. | X |
data: Retrieving user information
| Name | Type | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|---|
| property_keys | String[] |
Use this parameter to specify the scopes of user information to be requested in ["key1","key2"] format. | X |
Response
Kakao.API.request() returns Promise. If the promise is fulfilled, the user information is returned. For the detailed user information in response, refer to REST API.
Sample
Kakao.API.request({
url: '/v2/user/me',
})
.then(function(response) {
console.log(response);
})
.catch(function(error) {
console.log(error);
});
Additional feature
Retrieving specific user information
To request a specific user information, use the property_keys parameter.
Kakao.API.request({
url: '/v2/user/me',
data: {
property_keys: ['kakao_account.email', 'kakao_account.gender'],
},
})
.then(function(response) {
console.log(response);
})
.catch(function(error) {
console.log(error);
});
Store user information
Basic information
| Reference | App setting |
|---|---|
Kakao.API.request() |
Install Initialize |
| Permission | Prerequisite | Kakao Login | User consent |
|---|---|---|---|
| - | JavaScript key Activate Kakao Login Manage user properties |
Required | - |
Stores or updates additional user information on the Kakao platform to use in a service, which is called 'User properties'.
Request
To store or update the additional user information needed for the service, call the Kakao.API.request() function. The available parameters are below.
Pass the custom property keys and values that you want to update through properties under data. For example, if you want to update a user's clothing size, set properties to clothing_size: 'small'.
Parameter
| Name | Type | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|---|
| url | String |
Fixed to '/v1/user/update_profile'. |
O |
| data | Object |
Object that contains the parameter to be passed when requesting the API. | X |
data: Storing user information
| Name | Type | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|---|
| properties | Object |
User information that you want to update in {key:value} format. For key, check the registered property keys in [Kakao Login] > [Advanced] > [User Properties] on the app management page. |
O |
Response
Kakao.API.request() returns Promise. If the promise is fulfilled, the service user ID requested to update information is returned.
Sample
Kakao.API.request({
url: '/v1/user/update_profile',
data: {
properties: {
'${CUSTOM_PROPERTY_KEY}': '${CUSTOM_PROPERTY_VALUE}',
},
},
})
.then(function(response) {
console.log(response);
})
.catch(function(error) {
console.log(error);
});
Shipping address
Basic information
| Reference | App setting |
|---|---|
Kakao.Auth.selectShippingAddress()Kakao.API.request() |
Install Initialize |
| Permission | Prerequisite | Kakao Login | User consent |
|---|---|---|---|
| Required | JavaScript key Activate Kakao Login Manage consent items |
Required | Required: Shipping information (shipping_address) |
Select shipping address
Prompts the shipping address picker to allow users to select a shipping address and returns the selected shipping address ID.
Request
Call Kakao.Auth.selectShippingAddress().
Response
The function returns an addressId for the selected shipping address. Request Retrieve shipping address with the addressId to get the detailed shipping address.
Refer to Error code for the error cause.
Sample
// Select shipping address
Kakao.Auth.selectShippingAddress()
.then(function(selectedAddress) {
// Retrieve shipping address
return Kakao.API.request({
url: '/v1/user/shipping_address',
data: {
address_id: selectedAddress.address_id,
},
});
})
.then(function(response) {
console.log(response);
})
.catch(function(error) {
console.log(error);
});
Retrieve shipping address
Retrieves shipping addresses saved in the user's Kakao Account.
Request
Call the Kakao.API.request() function, and set url to /v1/user/shipping_address.
Specify the address ID to the address_id parameter.
Parameter
| Name | Type | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|---|
| url | String |
Fixed as '/v1/user/shipping_address'. | O |
| data | Object |
Object that contains the parameter to be passed when requesting the API. | X |
data: Retrieve shipping address
| Name | Type | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|---|
| address_id | Number |
Shipping address ID Used to specify an address ID to get a specific shipping address. |
X |
| from_updated_at | Number |
Modification time (updated_at) of the shipping address for retrieving shipping addresses across multiple pages. Set this value to the updated_at timestamp of the last shipping address from the previous page to fetch addresses updated before that time.In Unix timestamp format (unit: seconds). (Default: 0) Note: Shipping address pagination |
X |
| page_size | Number |
When retrieving shipping addresses over multiple pages, set the number of addresses to include per page. (Default: 10, Minimum: 2) Note: Shipping address pagination |
X |
Response
Kakao.API.request() returns Promise. If the promise is fulfilled, the user's shipping addresses are returned. For the detailed response fields, refer to REST API.
If not using Select shipping address API, the response may not include the shipping address when the user did not consent to the [Shipping information]. Refer to No shipping address in the response.
Refer to Error code for the error cause.
Sample
Kakao.API.request({
url: '/v1/user/shipping_address',
data: {
address_id: ${ADDRESS_ID},
},
})
.then(function(response) {
console.log(response);
})
.catch(function(error) {
console.log(error);
});
Retrieve consent details
Basic information
| Reference | App setting |
|---|---|
Kakao.API.request() |
Install Initialize |
| Permission | Prerequisite | Kakao Login | User consent |
|---|---|---|---|
| - | JavaScript key Activate Kakao Login Manage consent items |
Required | - |
Retrieves the detailed information of the scopes (consent items) that a user has agreed to. You can check all scopes set in [Kakao Login] > [Consent Items] on the app management page and the details of the scopes. If a user has consented to the scope before, the scope is included in the response even though your app is currently not using the scope.
Request
Call the Kakao.API.request() function.
Parameter
| Name | Type | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|---|
| url | String |
Fixed to /v2/user/scopes. |
O |
| data | Object |
Object that contains the parameters to be passed when requesting the API. | X |
data: Retrieving consent details
| Name | Type | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|---|
| scopes | String[] |
Used when you retrieve specific scopes only. List of scope IDs you want to retrieve. You can figure out each scope's ID in [Kakao Login] > [Consent Items] on the app management page. (Example: ["account_email","gender"]) |
X |
Response
Kakao.API.request() returns Promise. Refer to REST API for the detail.
Sample
Kakao.API.request({
url: '/v2/user/scopes',
})
.then(function(response) {
console.log(response);
})
.catch(function(error) {
console.log(error);
});
Additional feature
Check specific scopes
You can also designate the scopes you want to check the details by specifying the scopes parameter.
Kakao.API.request({
url: '/v2/user/scopes',
data: {
scopes: ['account_email', 'gender'],
},
})
.then(function(response) {
console.log(response);
})
.catch(function(error) {
console.log(error);
});
Revoke consent
Basic information
| Reference | App setting |
|---|---|
Kakao.API.request() |
Install Initialize |
| Permission | Prerequisite | Kakao Login | User consent |
|---|---|---|---|
| - | JavaScript key Activate Kakao Login Manage consent items |
Required | - |
Revokes the scope that a user has agreed to. You can only revoke the scope with "revocable":true among the scopes retrieved through the Retrieving consent details API. If you request to revoke the scope that is not revocable, an error is returned.
Request
Call the Kakao.API.request() function. Set the ID of the consent item to revoke in scopes parameter under data.
Parameter
| Name | Type | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|---|
| url | String |
Fixed to /v2/user/revoke/scopes. |
O |
| data | Object |
Object that contains the parameters to be passed when requesting the API. | O |
data: Revoking consent
| Name | Type | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|---|
| scopes | String[] |
List of scope IDs you want to revoke. You can revoke only the scope with "revocable":true among the scopes retrieved through the Retrieving consent details API.You can figure out each scope's ID in [Kakao Login] > [Consent Items] on the app management page. (Example: ["account_email","gender"]) |
O |
Response
Kakao.API.request() returns Promise. Refer to REST API for the detail.
Sample
Kakao.API.request({
url: '/v2/user/revoke/scopes',
data: {
scopes: ['account_email', 'gender'],
},
})
.then(function(response) {
console.log(response);
})
.catch(function(error) {
console.log(error);
});
Service terms
Basic information
| Reference | App setting |
|---|---|
Kakao.API.request() |
Install Initialize |
| Permission | Prerequisite | Kakao Login | User consent |
|---|---|---|---|
| Required: Kakao Sync | JavaScript key Activate Kakao Login Manage consent items Set Simple Signup |
Required | - |
This API is only allowed for the service that adopted Kakao Sync.
User consent for service terms must be managed directly by the service in accordance with the Service terms management policy. It is recommended to obtain consent for service terms not agreed to through Kakao Sync Simple Signup via a separate consent procedure. You can obtain consent for required service terms that the user has not agreed to or has revoked consent by the Get consent to desired service terms.
Retrieve consent details for service terms
Retrieves the service terms that a user has consented to.
Request
Call the kakao.API.request() function.
Parameter
| Name | Type | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|---|
| url | String |
Fixed to /v2/user/service_terms. |
O |
| data | Object |
Object that contains the parameter to be passed when requesting the API. | X |
data: Retrieving consent details for service terms
| Name | Type | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|---|
| result | String |
List of service terms to retrieve, use one of the followings.agreed_service_terms: List of service terms users have agreed to (default)app_service_terms: List of service terms enabled for the app |
X |
| tags | String |
Tags of service terms to retrieve, limited in the list specified by result.Pass multiple tags as a single comma ( ,) separated string. |
X |
Response
Kakao.API.request() returns Promise. If the promise is fulfilled, the information of the service terms to which a user consented to is returned. For the detailed response fields, refer to REST API.
Sample
Kakao.API.request({
url: '/v2/user/service_terms',
})
.then(function(response) {
console.log(response);
})
.catch(function(error) {
console.log(error);
});
Revoke consent for service terms
Revokes a service terms that a specific user has agreed to. Only service terms with a revocable value of true in the Retrieving consent details for service terms response can be revoked.
Request
Call the kakao.API.request() function. Specify the tags of the service terms you want to revoke consent for in tags under data.
Parameter
| Name | Type | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|---|
| url | String |
Fixed to /v2/user/revoke/service_terms. |
O |
| data | Object |
Object that contains the parameter to be passed when requesting the API. | O |
data: Revoke consent for service terms
| Name | Type | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|---|
| tags | String |
Service terms tags to revoke. Pass multiple tags as a single comma ( ,) separated string, refer to Example.Note: Only service terms with a revocable value of true in the Retrieving consent details for service terms response can be revoked. |
O |
Response
Kakao.API.request() returns Promise. If the promise is fulfilled, the information of the revoked service terms is returned. For the detailed response fields, refer to REST API.
Sample
Kakao.API.request({
url: '/v2/user/revoke/service_terms',
data: {
tags: 'test_tag1,test_tag2'
},
})
.then(function(response) {
console.log(response);
})
.catch(function(error) {
console.log(error);
});
Additional feature
Retrieving all service terms registered in app
To retrieve all service terms registered in app, set result under data to app_service_terms.
Kakao.API.request({
url: '/v2/user/service_terms',
data: {
result: 'app_service_terms',
},
})
.then(function(response) {
console.log(response);
})
.catch(function(error) {
console.log(error);
});
Retrieving specific service terms
To retrieve information of specific service terms, set tags under data to the IDs of the desired service terms.
Kakao.API.request({
url: '/v2/user/service_terms',
data: {
tags: 'test_tag1,test_tag2'
},
})
.then(function(response) {
console.log(response);
})
.catch(function(error) {
console.log(error);
});
Advanced: Manual signup
Basic information
| Reference | App setting |
|---|---|
Kakao.API.request() |
Install Initialize |
| Permission | Prerequisite | Kakao Login | User consent |
|---|---|---|---|
| Required | JavaScript key Activate Kakao Login |
Required | - |
The Manual signup API is only for the app with the Auto-link option disabled. Before using this API, check out when to use this API and the cautions in REST API.
The Manual signup API manually links a user with your app to complete signup when the Auto-link is disabled. To figure out if the currently logged-in user needs to be linked with your app, check the value of has_signed_up in the response of the Retrieving user information API and handle each case:
true: The user is already linked with your app. You do not need to call the Manual signup API.false: The user is not linked with your app. You must link the user with your app manually.null: Your app is using the Auto-link feature. You do not need to call the Manual signup API.
Request
Call the Kakao.API.request() function.
Parameter
| Name | Type | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|---|
| url | String |
Fixed to /v1/user/signup. |
O |
| data | Object |
Object that contains the parameter to be passed when requesting the API. | X |
data: Manual signup
| Name | Type | Description | Required |
|---|---|---|---|
| properties | Object |
Used when you want to store user properties when linking a user. (Example: {key:value})Refer to Manage user properties and Store user information. |
X |
Response
Kakao.API.request() returns Promise. If the promise is fulfilled, the user's service user ID is returned. To check the request result in detail, call the Retrieving user information API again and see the value of has_signed_up and properties.status in the response.
Sample
Kakao.API.request({
url: '/v1/user/signup',
})
.then(function(response) {
console.log(response);
})
.catch(function(error) {
console.log(error);
});
Additional feature
Update additional information
If you want to store the user's information when the user is linked to your app, pass properties in data.
Kakao.API.request({
url: '/v1/user/signup',
data: {
properties: {
'${CUSTOM_PROPERTY_KEY}': '${CUSTOM_PROPERTY_VALUE}',
},
},
})
.then(function(response) {
console.log(response);
})
.catch(function(error) {
console.log(error);
});